The secret of EV charger power: How 7kW to 250kW affects your travel experience
Today, as the penetration rate of new energy vehicles exceeds 35%, the power of EV chargers has become a core indicator that affects consumers’ car purchase decisions. This article deeply analyzes the technical logic behind the power parameters of EV chargers, reveals the applicable scenarios and market trends of different power levels, and helps you quickly identify the most suitable charging solution.
Current EV charger market presents a clear three-polarization pattern:
– Basic slow charging (7kW-22kW): Suitable for home EV chargers and public slow charging stations, using single-phase AC technology, suitable for nighttime charging scenarios. Data shows that in 2023, the market share of home EV chargers will reach 62%, of which 7kW products will still be the mainstream.
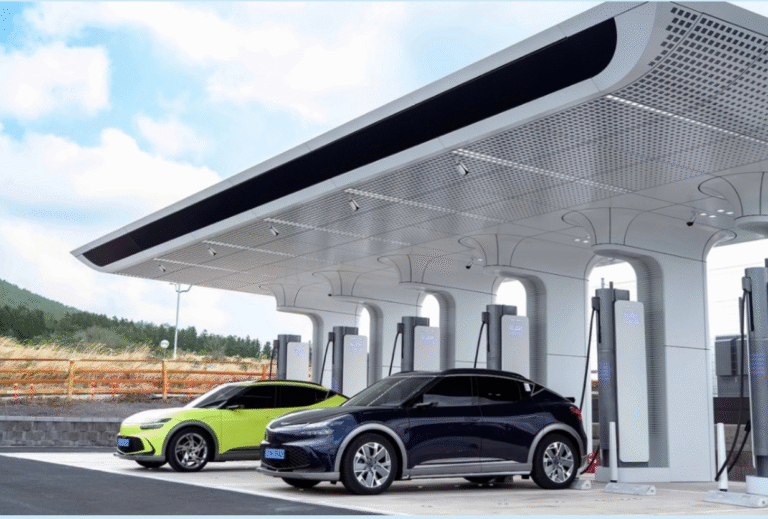
– Super fast charging (50kW-150kW): represents the direction of technological breakthroughs. The power of a single Tesla V4 super EV charger reaches 250kW, which can achieve 300 kilometers of charging in 8 minutes . However, it should be noted that ultra-high voltage charging can easily double the pressure on battery thermal management .
– Mobile fast charging (43kW-150kW): The 120kW liquid-cooled mobile charging vehicle launched by NIO Power can still output stably in extreme environments of -30℃ to 60℃, redefining the standard for outdoor energy replenishment .
Question session: Do you value the stability of home charging more, or the convenience brought by fast charging ?
2. Technology decoding: Five core breakthroughs behind power improvement
1. DC technology iteration: From single-channel 200V to 600V high-voltage platform, with silicon carbide ( SiC ) semiconductor refrigeration module, the charging efficiency is increased by 40%
2. Thermal management system innovation: CATL’s latest patent shows that the peak charging temperature can be controlled within 45°C through the coordinated control of phase change materials (PCM) and liquid cooling pipelines.
3. Communication protocol upgrade: The national standard GB/T 20234-2022 requires support for CCS2/CHAdeMO dual protocols, and the compatibility rate is increased to 98%.
4. Intelligent diagnosis system: Teladian’s latest V5.0 version can monitor 12 parameters such as charging gun temperature rise and current fluctuation in real time, with a fault warning accuracy rate of 92%.
5. Modular design: Huawei’s EBP super charging module is “plug and play”, and the deployment cycle of a single station is shortened from 15 days to 72 hours
Question section: In the face of technological iterations, should ordinary car owners pay more attention to parameter improvements or the improvement of service support?
3. Market Insights: Power Demand Shows Three Typical Characteristics
– Obvious differentiation in scenarios: Home scenarios tend to favor 7kW economical models (cost reduction of 60%), while public scenarios pursue 150kW ( the ratio of vehicles to EV chargers is optimized to 1:4)
– Significant regional differences: The penetration rate of fast EV chargers in the Yangtze River Delta region reached 38%, 27 percentage points higher than that in the southwest region (China Charging Alliance 2023Q2 data)
– Cost-sensitive critical point: When the cost per kilowatt-hour exceeds 0.8 yuan, users are more inclined to choose slow charging ( survey by State Grid Research Institute )
Question session: Given the current charging costs, how much premium are you willing to pay to shorten charging time?
4. Future Trends: Power Competition Will Trigger Triple Changes
1. Coordinated development of vehicles and EV chargers: BYD’s latest plan shows that by 2025, the perfect adaptation of 150kW superEV chargers and blade batteries will be achieved, and the battery life attenuation rate will be controlled within 3%.
2. Grid stress test: China Southern Power Grid has launched a “power leap plan” with the goal of connecting 100 200kW supercharging stations to the grid by 2024 , with the proportion of supporting energy storage increasing to 30%.
EV chargers installed after 2025 must support an 800V high-voltage platform, and the power limit will exceed 300kW
Question section: In the face of power surge, which should be prioritized: grid carrying capacity or battery safety?
5. Purchase Guide: Hidden Value Behind Power Parameters
– Battery life matching: It is recommended to choose 150kW fast charging for lithium iron phosphate batteries, and ternary lithium batteries are suitable for 200kW super charging (battery thermal runaway risk comparison)
– Frequency of use: For users who charge more than once a day, a home 7kW + mobile fast charging car combination is recommended
– Cost accounting: Based on an average of 1,200 charging times per year, a 50kW fast EV charger saves about 800 hours of time cost compared to a 7kW slow EV charger (valued at 40,000 yuan at an hourly wage of 50 yuan)
From 7kW basic slow charging to 250kW supercharging technology, the EV charger power revolution is reshaping the travel ecosystem. It is recommended that car owners establish a ” scenario-based selection” mindset: daily commuting prioritizes economy, long-distance travel focuses on energy replenishment efficiency , and emergency scenarios rely on mobile charging. At the same time, we must be vigilant about the safety hazards brought about by the power jump, and choose high-quality equipment that has passed IP67 waterproof and FCC electromagnetic compatibility certification. In the next three years, with the popularization of 800V high-voltage platforms, charging power will exceed the 400kW mark, but how to balance technological innovation and safety experience still requires the industry to continue to explore.