Classification Of EV Charger (EVSE)
EV Charger is a common name for Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), which is a tool used to supplement electric energy for electric vehicles.
The power battery of an electric vehicle can only receive direct current (DC) voltage, while the power grid/household socket provides alternating current, which requires AC-DC conversion before charging the battery.
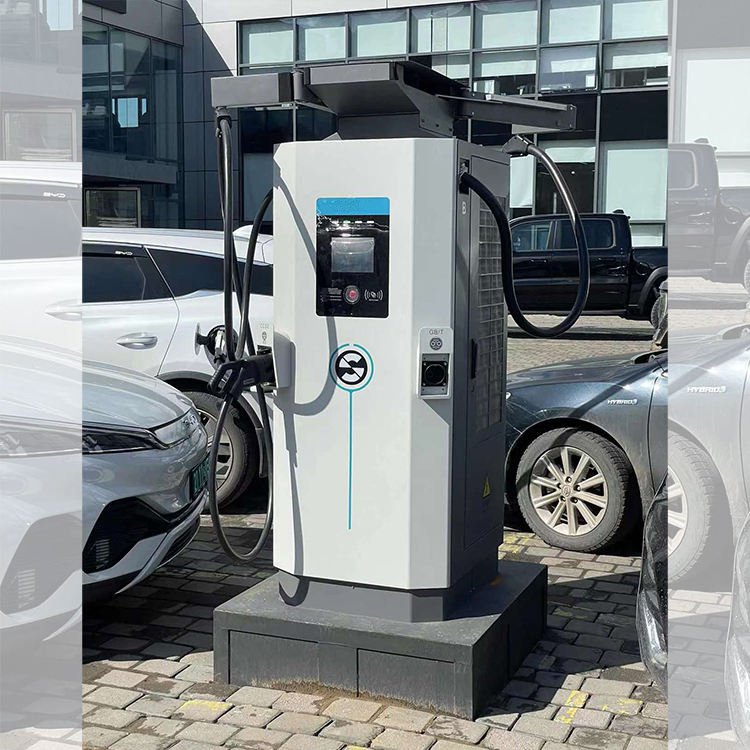
The direct current (DC) charger integrates a power module, which performs AC-DC conversion inside the charger and outputs DC power to charge the battery.
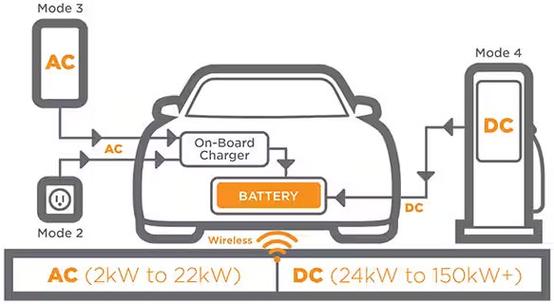
The Alternating Current (AC) station supplies power to the onboard charger (OBC), which performs AC-DC rectification and conversion to charge the power battery.
A direct current (DC) charging station is a device that bypasses the on-board charger (OBC) and directly charges the battery.
Voltage/Mode Classification
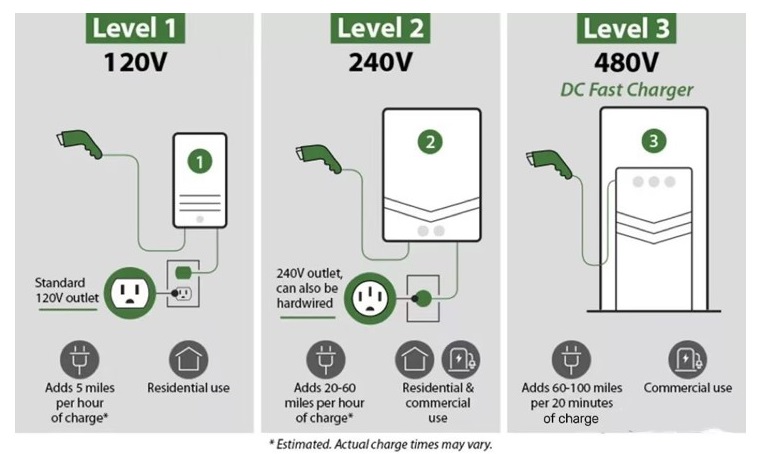
The United States generally uses Level 1/2/3 Classification;
Level 1/2/3 mainly distinguishes charging Voltage at the input end of the charger.
Level 1 refers to charging stations that are directly powered by American household plugs (single-phase) 120V, with a power of 1.4-1.9kW;
Level 2 refers to the use of American household high voltage 208/230V (European)/240V AC charging stations with a power of 3-19.2kW;
Level 3 refers to a DC charging station.

Outside of the United States,for example Europe, Mode 1/2/3/4 is generally used for differentiation;
The classification of Mode 1/2/3/4 mainly depends on whether the charging station has communication with the electric vehicle.
Mode 1 refers to the use of wires to charge a car, with one end being a regular plug connected to a wall socket and the other end being a charging plug on the car side. There is no communication between the car and the charging device (which actually does not have any equipment), and it is now prohibited in many countries.
Mode 2 refers to a portable AC charging station that is not fixedly installed and comes with vehicle to station communication;
Mode 3 refers to other AC charging stations with fixed installation (wall mounted or column mounted) and vehicle to station communication;
Mode 4 specifically refers to fixed installation of DC charging stations, and there must also be vehicle-charger communication.
Charging standard classification
There is no unified global standard for the charging interface of electric vehicles, just like the complex and diverse charging interfaces of mobile phones before 2012.
Charging guns and vehicle charging interfaces of different standards cannot be used interchangeably.
Overall, the current standards are developed by countries in the automotive industry and important market countries such as Europe, the United States, Japan, and China.

Power classification
Commonly encountered power ratings for charging stations include:
- 3kW portable units (AC)
- 7/11kW wall-mounted Wallboxes (AC)
- 22/43kW operational pillar units (AC)
- DC charging stations ranging from 20-350kW, even up to 500kW
The maximum power of a charging station refers to the highest possible power it can deliver to a battery. This is calculated as voltage (V) × current (A), and for three-phase systems, multiplied by 3.
The power of DC charging stations primarily depends on their internal power modules (connected in parallel internally). Currently, the mainstream modules are 25/30kW, so the power of DC charging stations is typically a multiple of these module powers. However, compatibility with the charging power of electric vehicle batteries must also be considered. This is why DC charging stations of 50/100/120kW are very common in the market.
EV CHARGER CLUB Provides all kinds of charging equipments.Explore our range of DC fast chargers and smart charging solutions designed for global markets. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your sustainability goals.